The following diagram shows the stages of the Data Entry Audit process:
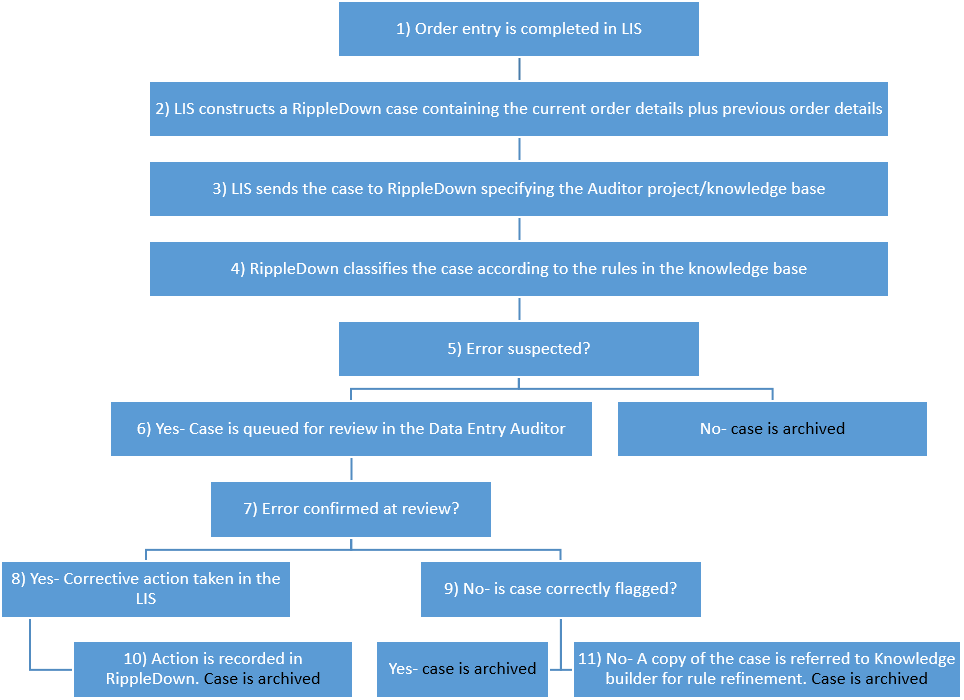
- The Data Entry Audit process starts as soon as a data entry operation is complete, either a manually entered order request, or an order request made electronically.
- The Laboratory Information System constructs a RippleDown case in the same format as a case that requires a clinical interpretation The typical data items required are specified later in this document.
- The Laboratory Information System sends the case to RippleDown, with a code identifying the Data Entry Knowledge Base (similar to the “panel code” used for cases requiring clinical interpretation). More than one Knowledge Base may be deployed, if necessary.
- RippleDown classifies the case according to the Data Entry Knowledge Base. This Knowledge Base is created and maintained by the Data Entry Manager using the RippleDown Knowledge Builder console. Rules in the Knowledge Base check the current and previous episode information, and provide a flag indicating if the data entry order is at risk of being in error, or not.
- If the data entry order is at risk of being in error, the case is sent to a queue on the Data Entry Auditor console, for review by Data Entry Auditors. If the order not classified as being at risk by the Knowledge Base, it is simply temporarily archived in the RippleDown archive case list.
- The particular queue the case is sent to will depend on the type of potential error. For example, there may be a queue dedicated to billing problems only, whereas another queue may be used for general data entry errors such as a missing copy doctor missing. The definition of queues, and the allocation of error types to various queues, is determined by the Data Entry Knowledge Base. Cases indicating orders that are at risk are continually queued to the Data Entry Auditor console, and the number waiting to be reviewed on each type of queue can be seen at any time.
- Several times a day, the senior Data Entry staff review the cases that have been flagged, using the Data Entry Auditor console. The console shows the current order details, the previous order details, and the reason why this case was flagged by the Knowledge Base. Several queues may be reviewed simultaneously by different staff. Individual queues can also be reviewed simultaneously by more than one operator.
- When reviewing the flagged cases, if an order is found to be in error, the Data Entry staff take corrective action using the Laboratory Information System facilities. Both the Data Entry Auditor console and the Laboratory Information System console will be hosted on the Data Entry staff’s workstation.
- If there is no error confirmed at this stage then it needs to be established whether the case should have been flagged at all.
- After corrective action is taken, this action is recorded by the Auditor and a copy of the case is automatically sent to the Knowledge Builder application. This allows later review of the erroneous request for training purposes. It also automatically updates the performance statistics, allowing classification of the type of error that was found.
- If no corrective action needed to be taken, it is possible that the case was incorrectly queued to the Auditor console. If so, the Data Entry staff will have the option to queue the case to the RippleDown Knowledge Builder rejected case list where rules can be added to ensure that this type of case is not flagged in the future.
